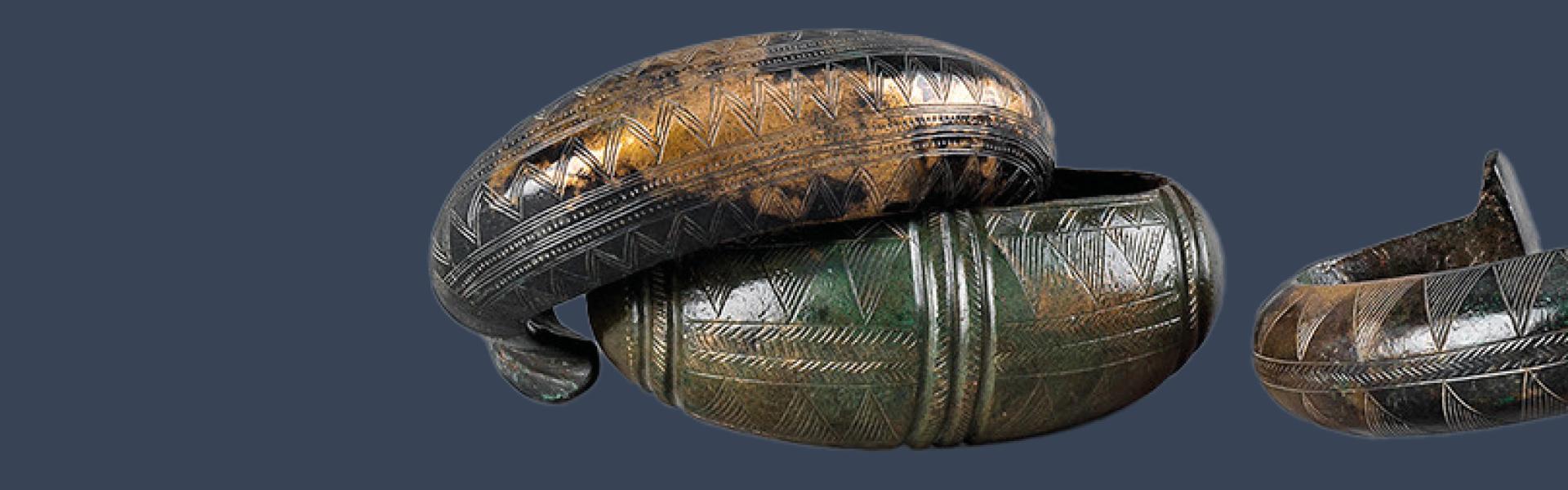
The Bronze Age
The Bronze Age marks an evolution rather than a break with the Neolithic.
The Bronze Age marks an evolution rather than a break with the Neolithic. There was a diversification and even an increased social hierarchy, largely due to the appearance and development of bronze metallurgy. Bronze was easy to hoard and recycle, and was a source of rivalry and conflict.
Bronze is an easily hoarded and recycled resource, but it is also a source of rivalry and conflict. Ores and metal objects were part of various supply and exchange networks that crossed the whole of Europe.
Craftsmen became specialised, and the man-at-arms and the warrior chief asserted their pre-eminence in a society that was still rural. The struggle for social and economic supremacy led to sumptuous production for the use of the powerful or the gods, but also to the multiplication of warehouses, symptoms of insecurity and instability.
Les objets
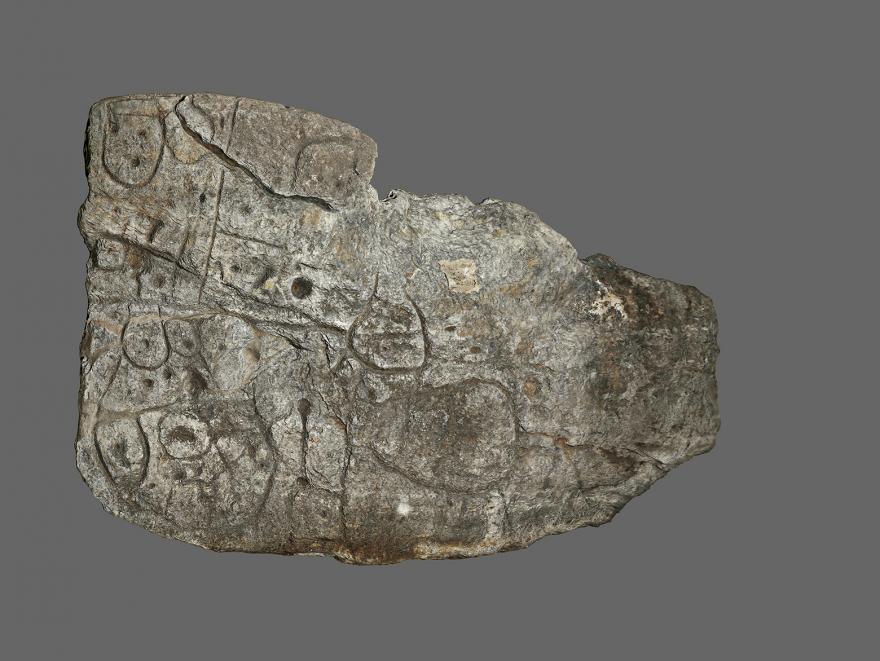
Mégalithe
Dalle gravée de Saint Bélec
Saint-Bélec, Leuhan (Finistère)
2200 - 2000 avant notre ère

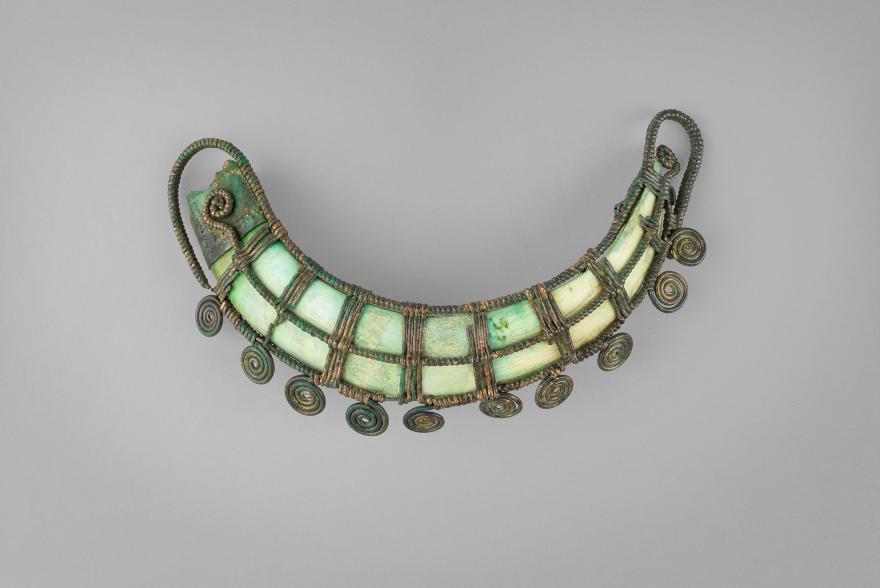
parure
La Dame de La Colombine
Sépulture 101 de la nécropole de Champlay (Yonne)
Fouille G. Bolnat, 1938
Début du Bronze final (1300–1200 av. J.-C.)

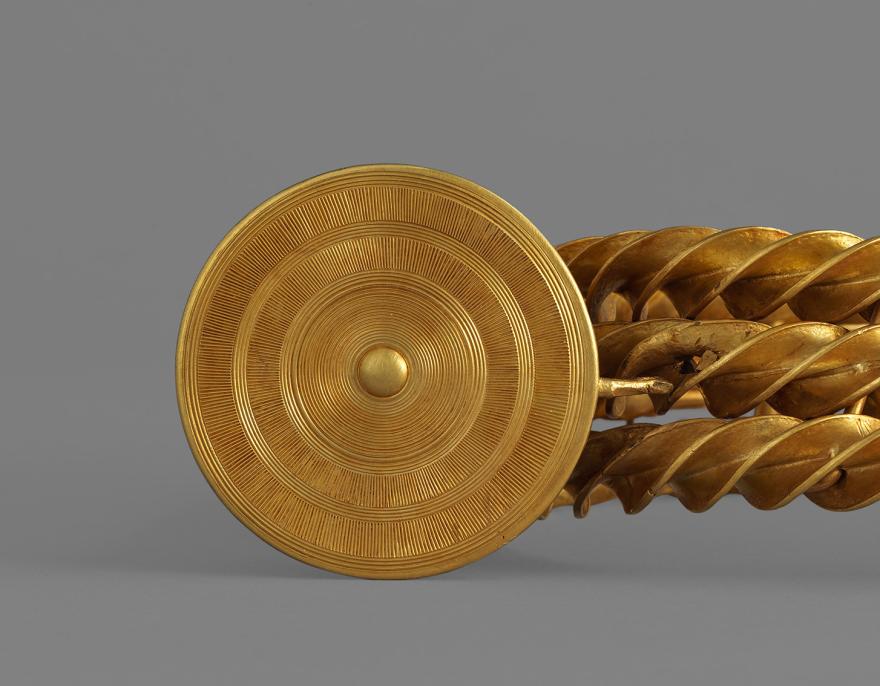
dépôt
Dépôt de parures en or de Guînes
Guînes (Pas-de-Calais)
Bronze final, 1200-800 av. J.-C.
Acquisition
Découverte fortuite (1985) Achat (2003)

dépôt
Le dépôt de Larnaud
Larnaud (Jura),Les Genettes
vers 1000 - 900 av. J.-C.
Acquisition
Achat à un particulier, 1867

parure
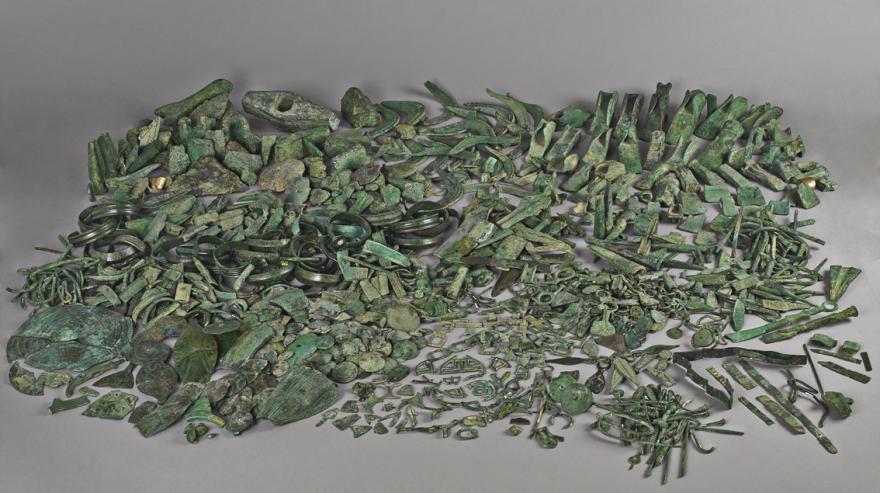
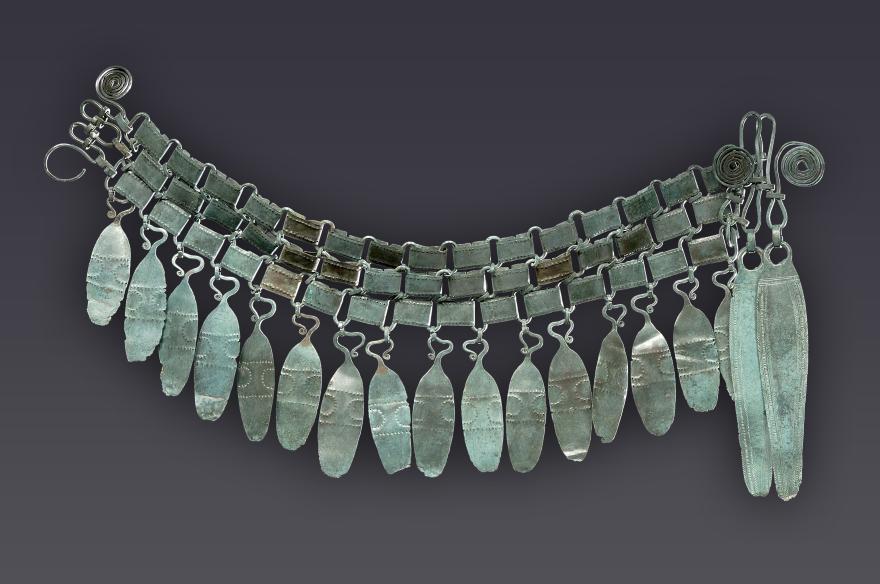
Ceinture articulée en bronze du Theil
Le Theil, Billy (Loir-et-Cher), dépôt de la Fosse-aux-prêtres
Bronze final, vers 1 100 avant J.-C.

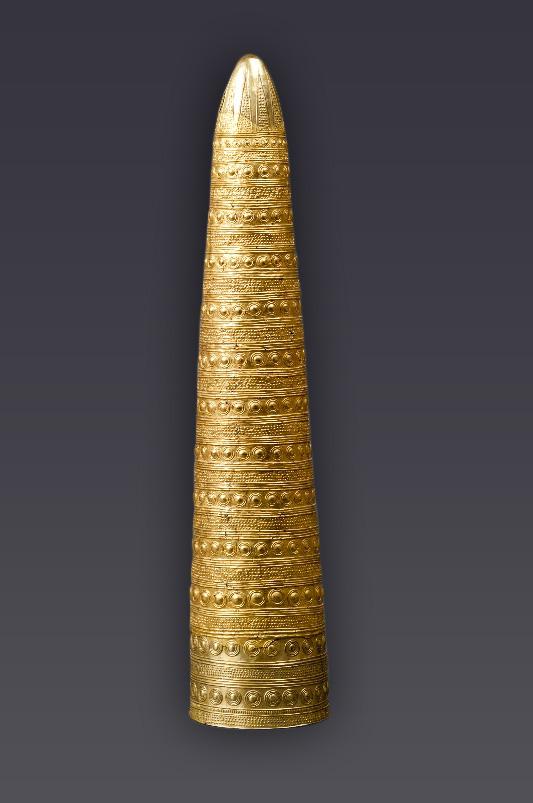
Objet emblématique
Cône d'Avanton
Avanton (Vienne)
1 500 - 1200 avant J.-C.

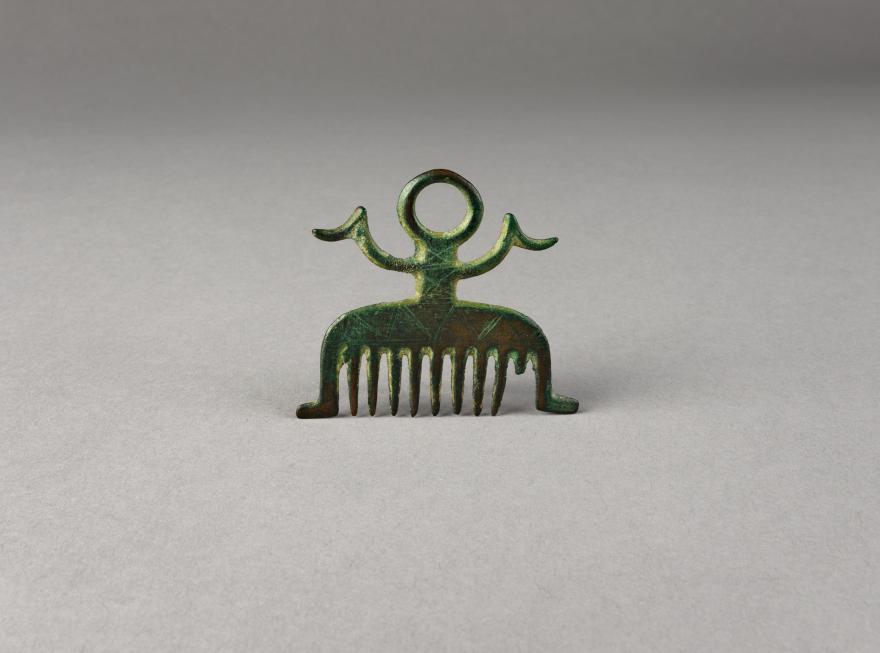
Bijoux
Pendentif en forme de peigne de Dôle
Provenance inconnue (Jura)
Bronze final, 1100-1000 av. J.-C.

dépôt
Le dépôt de Vaudrevange
Vaudrevange / Wallerfangen (Sarre, Allemagne)
IXe av. J.-C.

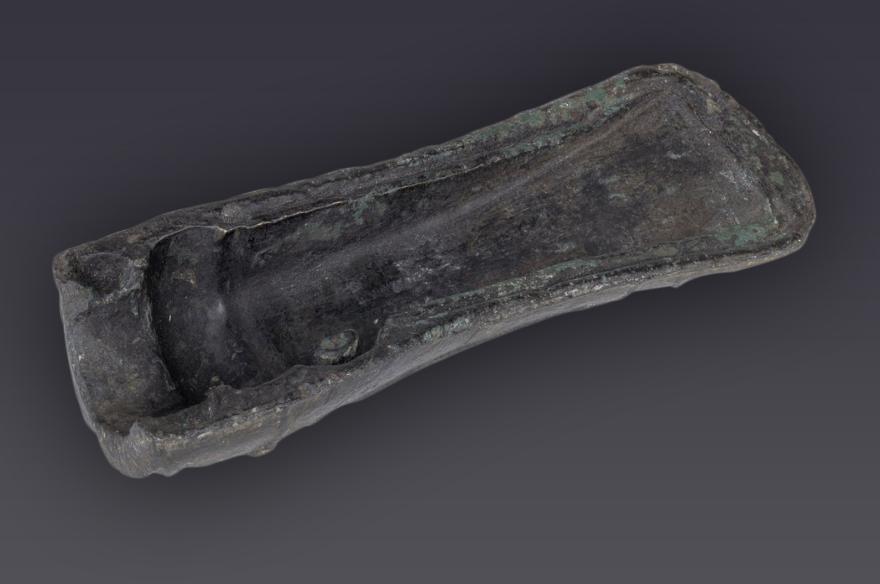
Outils
Moules de hache avec leurs noyaux
Dépôt de Thiais (Val de Marne)
Bronze final 3b (IXe siècle av. J.-C.)
Acquisition
Don de la ville de Paris - 1935

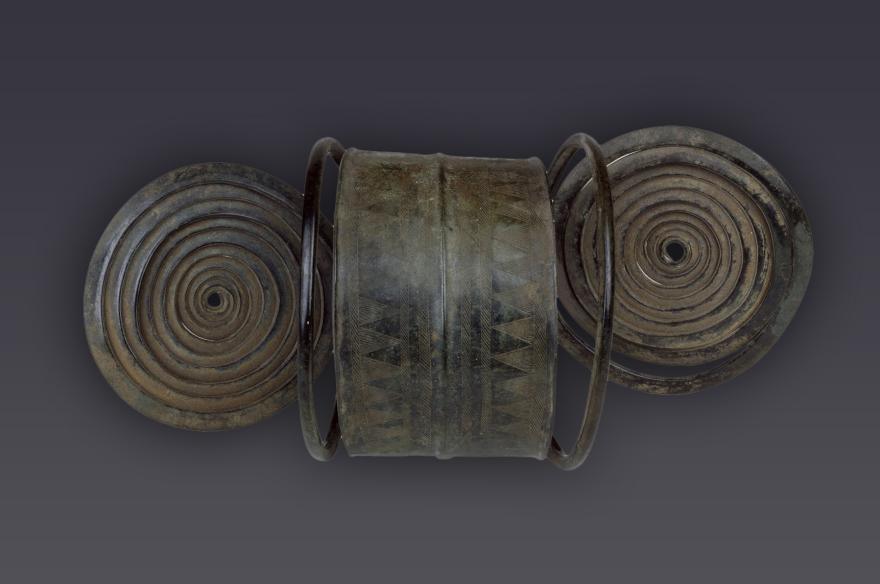
parure
Jambières à spirales
Veuxhaulle (Côte d'or)
Bronze final I-IIa (1 300 - 1 100 avant J.-C.)
Acquisition
Don Flouest, 1882

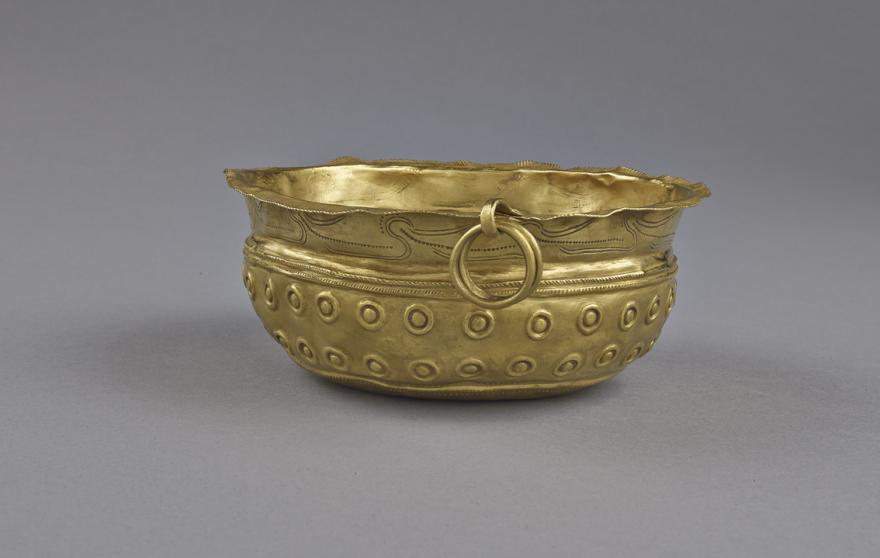
Vaisselle
Tasse en or de Paimpont
Lisière de la forêt de Paimpont, au bord de la rivière Aff (Ile et Vilaine), vers 1880

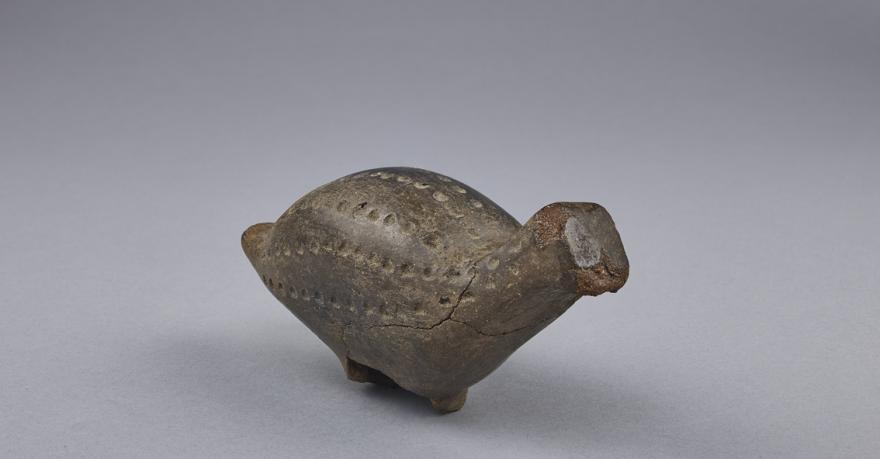
figurine
Figurine d’oiseau en terre cuite de Tigy
Le Bois des Hauts (lieu-dit) (Loiret)
XIIe-Xe siècle avant J.-C.

Armes
The Marmesse cuirass
This breastplate in sheet bronze is part of a collection of similar pieces discovered in several stages at Marmesse (Haute-Marne), at the site known as “Petit Marais” (Small Marsh). In 1974 the first three cuirasses were discovered, placed one inside the other. They were unearthed by chance during terracing work in a sand quarry. Fragments of other cuirasses were discovered subsequently, and an archaeological survey was carried out in 1980, enabling the collection to be completed.In all, seven cuirasses were found at Marmesse, representing part of a votive hoard probably linked to the presence of a spring. The circumstances of the discovery of these defensive weapons, and the absence of any specific archaeological context, explain the imprecise dating, which is based purely on typological and stylistic considerations.The discoveries at Marmesse are part of an important series of hoards, which, at this pivotal time between the Bronze Age and the Iron Age, express in different ways the prestige and the power of a warrior elite. As well as carrying these prestigious defensive weapons, warriors wore helmets and greaves (leg protectors). Attacking weaponry consisted of a sword and a spear. This equipment evokes in some way the “bronze-clad” warriors described by Homer. We should not forget that the Trojan War took place at the end of the Bronze Age.

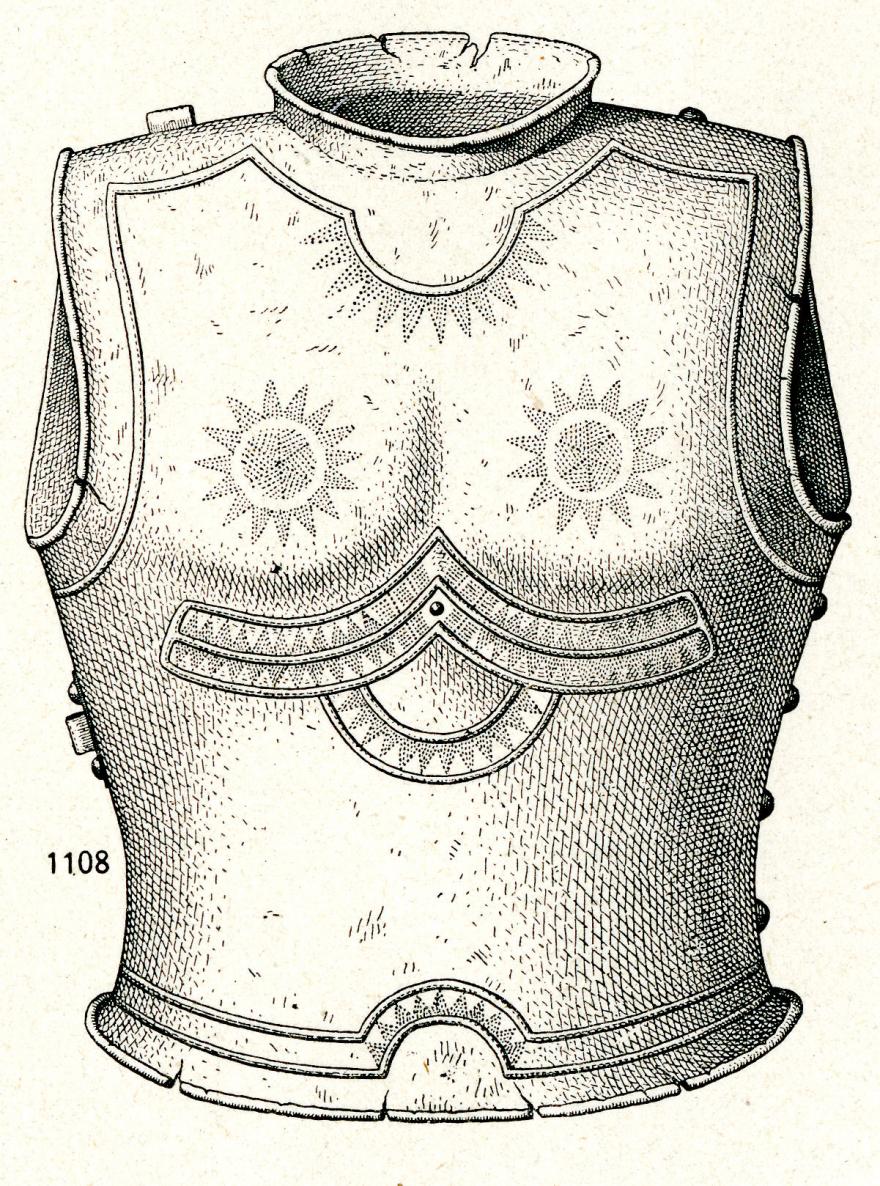
Armes
La cuirasse de Saint-germain-du-Plain
Saint-Germain-Plain (Saône-et-Loire)
Âge du Bronze final, 1200 -1100 avant J.-C.
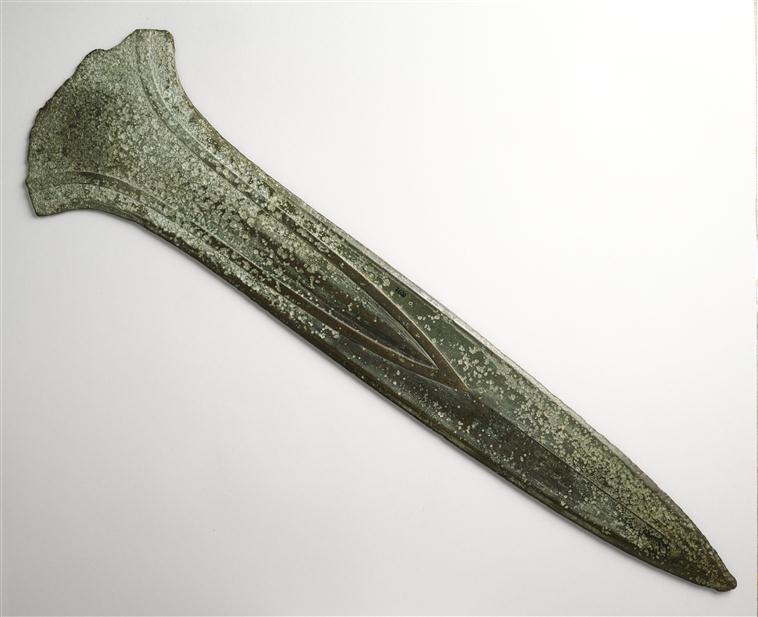
Armes
L'épée de Plougrescant
Plougrescant (côtes d'Armor)
Bronze moyen, vers 1600-1300 av J.-C.

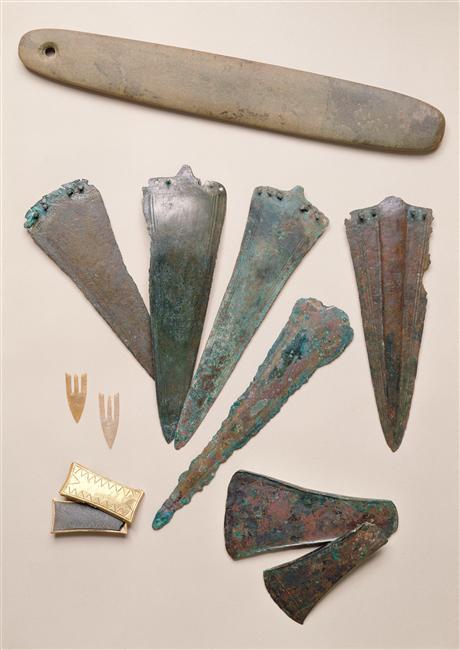
dépôt
Sépulture dite “princière” de La Motta
Lieu-dit “Bel-Air” (anciennement “La Motta”), Lannion (Côtes-d’Armor)
2000-1800 av. J.-C

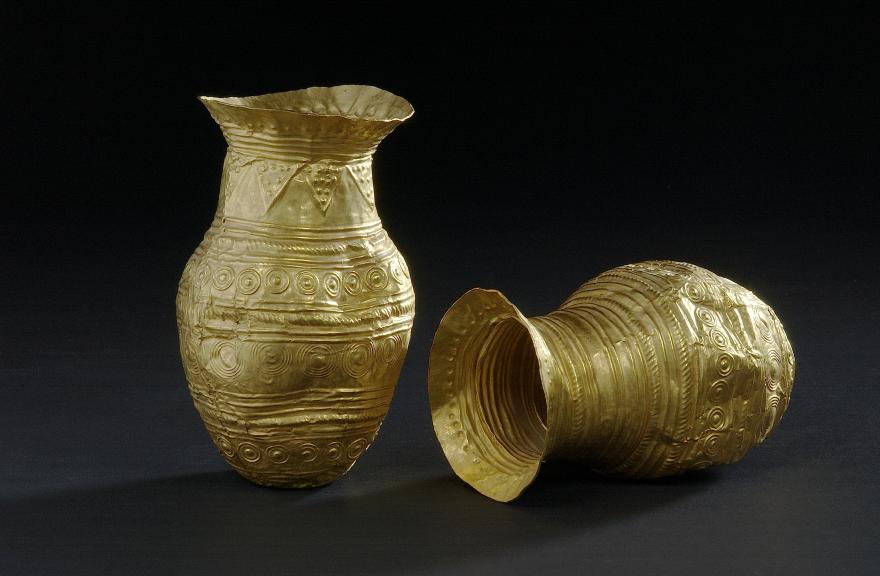
Vaisselle
Gold Vessels and Jewellery
The first gold objects in France, the oldest in the whole of Western Europe, appeared in the South of France at the end of the Neolithic Period.Since the 3rd millennium, river silt has been panned to find flakes and nuggets of this precious metal. It was in the Bronze Age that gold artefacts became abundant and often impressive. As most of them have been found in hoards, we can conclude that these were votive offerings. This is true of the collection discovered at Villeneuve-Saint-Vistre (Marne) in 1910, at the place known as the “Sandstone Field”.Beneath an enormous 2 m2 block, the discovery was made of two small gold goblets, two open, ribbon-shaped bracelets, sixteen double gold wires and three rings, one of which has now disappeared. The collection was perhaps placed in a ceramic container, a few shards of which have been found. The association of jewellery and ceremonial vessels in gold is quite rare in France.

Céramique
Le dépôt céramique de la grotte funéraire de Rancogne
Grotte de Rancogne (Charente)
Âge du Bronze final - 10e- 9e siècle av. J.-C.


